| Mars Resources |
|
Mars Introduction The Surface of Mars Mars Pathfinder Mission Martian Volcanoes Martian Clouds The Face on Mars Magnetic Stripes Preserve Record of Ancient Mars Mars Image Gallery |
 An impact basin deep enough to swallow
Mount Everest and
surprising slopes in Valles Marineris highlight a global map
of Mars that will influence scientific
understanding of the red planet for years.
An impact basin deep enough to swallow
Mount Everest and
surprising slopes in Valles Marineris highlight a global map
of Mars that will influence scientific
understanding of the red planet for years.
Generated by the Mars Orbiter Laser Altimeter (MOLA), an instrument aboard NASA's Mars Global Surveyor, the high- resolution map represents 27 million elevation measurements gathered in 1998 and 1999. The data were assembled into a global grid with each point spaced 37 miles (60 kilometers) apart at the equator, and less elsewhere. Each elevation point is known with an accuracy of 42 feet (13 meters) in general, with large areas of the flat northern hemisphere known to better than six feet (two meters).
"This incredible database means that we now know the topography of Mars better than many continental regions on Earth," said Dr. Carl Pilcher, Science Director for Solar System Exploration at NASA Headquarters, Washington, DC. "The data will serve as a basic reference book for Mars scientists for many years, and should inspire a variety of new insights about the planet's geologic history and the ways that water has flowed across its surface during the past four billion years."
"The full range of topography on Mars is about 19 miles (30 kilometers), one and a half times the range of elevations found on Earth," noted Dr. David Smith of NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, MD, the principal investigator for MOLA and lead author of a study to be published in the May 28, 1999, issue of Science.
"The most curious aspect of the topographic map is the striking difference between the planet's low, smooth Northern Hemisphere and the heavily cratered Southern Hemisphere," which sits, on average, about three miles (five kilometers) higher than the north, Smith added. The MOLA data show that the Northern Hemisphere depression is distinctly not circular, and suggest that it was shaped by internal geologic processes during the earliest stages of martian evolution.
 The massive Hellas impact basin in the Southern
Hemisphere is another striking feature of the map. Nearly
six miles (nine kilometers) deep and 1,300 miles (2,100
kilometers) across, the basin is surrounded by a ring of
material that rises 1.25 miles (about two kilometers) above
the surroundings and stretches out to 2,500 miles (4,000
kilometers) from the basin center.
The massive Hellas impact basin in the Southern
Hemisphere is another striking feature of the map. Nearly
six miles (nine kilometers) deep and 1,300 miles (2,100
kilometers) across, the basin is surrounded by a ring of
material that rises 1.25 miles (about two kilometers) above
the surroundings and stretches out to 2,500 miles (4,000
kilometers) from the basin center.
This ring of material, likely thrown out of the basin during the impact of an asteroid, has a volume equivalent to a two-mile (3.5-kilometer) thick layer spread over the continental United States, and it contributes significantly to the high topography in the Southern Hemisphere.
The difference in elevation between the hemispheres results in a slope from the South Pole to North Pole that was the major influence on the global-scale flow of water early in martian history. Scientific models of watersheds using the new elevation map show that the Northern Hemisphere lowlands would have drained three-quarters of the martian surface.
 On a more regional scale, the new data show that the
eastern part of the vast Valles Marineris canyon slopes away
from nearby outflow channels, with part of it lying a half-
mile (about one kilometer) below the level of the outflow
channels.
On a more regional scale, the new data show that the
eastern part of the vast Valles Marineris canyon slopes away
from nearby outflow channels, with part of it lying a half-
mile (about one kilometer) below the level of the outflow
channels.
"While water flowed south to north in general, the data clearly reveal the localized areas where water may have once formed ponds, " explained Dr. Maria Zuber of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, MA, and Goddard.
The amount of water on Mars can be estimated using the new data about the south polar cap and information about the North Pole released last year. While the poles appear very different from each other visually, they show a striking similarity in elevation profiles. Based on recent understanding of the North Pole, this suggests that the South Pole has a significant water ice component, in addition to carbon dioxide ice.
The upper limit on the present amount of water on the martian surface is 800,000 to 1.2 million cubic miles (3.2 to 4.7 million cubic kilometers), or about 1.5 times the amount of ice covering Greenland. If both caps are composed completely of water, the combined volumes are equivalent to a global layer 66 to 100 feet (22 to 33 meters) deep, about one-third the minimum volume of a proposed ancient ocean on Mars.
During the ongoing Mars Global Surveyor mission, the MOLA instrument is collecting about 900,000 measurements of elevation every day. These data will further improve the global model, help engineers assess the area where NASA's Mars Polar Lander mission will set down on Dec. 3, and aid the selection of future landing sites. MOLA was designed and built by the Laser Remote Sensing Branch of the Laboratory for Terrestrial Physics at Goddard. The Mars Global Surveyor mission is managed for NASA's Office of Space Science, Washington, DC, by the Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, CA, a division of the California Institute of Technology.
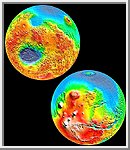
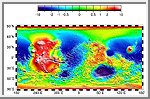 Topography Map of Mars
Topography Map of Mars
Map of Mars' topography with zonal spherical harmonic degree 1
(COM/COF offset along the polar z-axis axis) removed. The
projection is rectangular to show topography from pole to
pole. Note the general similarity in elevation between the
northern and southern hemispheres. The figure highlights
the two other significant components of martian topography:
the Tharsis province and the Hellas impact basin. Here we
have not removed shorter-wavelength topographic features,
including those comprising the dichotomy boundary scarp.
(Courtesy GSFC/NASA)
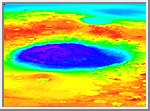
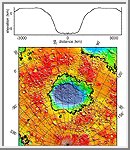 Regional Topographic Model of the Hellas Basin
Regional Topographic Model of the Hellas Basin
Regional topographic model of the Hellas basin. (Top)
Azimuthally-averaged radial topography used in the calculation of
infilling the basin with surrounding material postulated to have
been excavated from it. (Bottom) Color-coded topography
plotted in an equal-area projection. The black lines correspond
to zero-elevation contours.
(Courtesy GSFC/NASA)
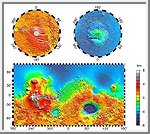 Maps of Mars Global Topography
Maps of Mars Global Topography
The lower map projection is Mercator to 70° latitude and the
upper polar maps are stereographic with the
south pole at left and north pole at right. Note the elevation
difference between the northern and southern hemispheres. The
Tharsis volcano-tectonic province is centered near the equator
in the longitude range 220° E to 300° E and contains the vast
east-west trending Valles Marineris canyon system and several
major volcanic shields including Olympus Mons.
(Courtesy GSFC/NASA)
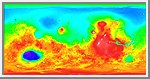
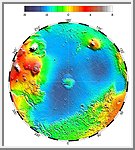 Lambert Equal-Area Projection of Pole-to-Equator
Lambert Equal-Area Projection of Pole-to-Equator
Lambert equal-area projection of pole-to-equator topography
in the northern hemisphere. The Utopia Basin is the circular
depression (in light blue) in the upper right.
(Courtesy GSFC/NASA)
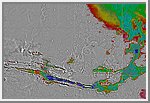
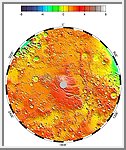 Polar Stereographic Projection
Polar Stereographic Projection
This image is a polar stereographic projection of Martian topography from
latitude 55° S to the pole.
(Courtesy GSFC/NASA)