|
COMETS EARTH JUPITER KUIPER BELT MARS MERCURY METEORITES NEPTUNE OORT CLOUD PLUTO SATURN SOLAR SYSTEM SPACE SUN URANUS VENUS ORDER PRINTS
PHOTO CATEGORIES SCIENCEVIEWS AMERICAN INDIAN AMPHIBIANS BIRDS BUGS FINE ART FOSSILS THE ISLANDS HISTORICAL PHOTOS MAMMALS OTHER PARKS PLANTS RELIGIOUS REPTILES SCIENCEVIEWS PRINTS
|
Related Documents
Download Options
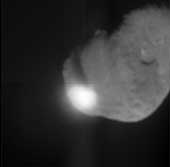
When NASA's Deep Impact probe collided with Tempel 1, a bright, small flash was created, which rapidly expanded above the surface of the comet. This flash lasted for more than a second. Its overall brightness is close to that predicted by several models. After the initial flash, there was a pause before a bright plume quickly extended above the comet surface. The debris from the impact eventually cast a long shadow across the surface, indicating a narrow plume of ejected material, rather than a wide cone. The Deep Impact probe appears to have struck deep, before gases were heated and explosively released. The impact crater was observed to grow in size over time. A preliminary interpretation of these data indicate that the upper surface of the comet may be fluffy, or highly porous. The observed sequence of impact events is similar to laboratory experiments using highly porous targets, especially those that are rich in volatile substances. The duration of the hot, luminous gas phase, as well as the continued growth of the crater over time, all point to a model consistent with a large crater. This image was taken by Deep Impact's medium-resolution camera. |