







|
| Introduction |
|---|
Although not as pronounced as on Earth, clouds are common features on Mars. The Martian atmosphere has only a trace of water vapor; however, the temperature and pressure is such that the atmosphere is usually close to saturation and produces clouds. Even from Earth based telescopes, clouds have been observed by transient brightening on the surface of Mars. Numerous cloud patterns have been seen from the Marineer and Viking spacecraft and have been classified into various categories (Carr, 1981; French et al. 1981):
| Views of Martian Clouds |
|---|
 Cyclonic Disturbances
Cyclonic Disturbances
Along the edge of the polar cap, cyclonic disturbances are common during
the late summer and fall. This storm system is located at the edge of
the northern polar cap. In the foreground, frost can be seen as bright
areas.
(Courtesy Calvin J. Hamilton)
 Lee Wave
Lee Wave
This is a good example of a lee wave associated with an impact
crater. Note the wave periodicity in the clouds.
(Courtesy Calvin J. Hamilton)
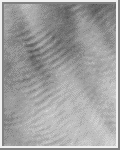 Wave Clouds
Wave Clouds
Wave clouds usually occur at the lee of a large obstacle. They are often
found at the edge of the polar cap, and in the Tharsis and Lunae Planum
regions.
(Courtesy Calvin J. Hamilton)
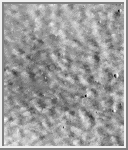 Cloud Streets
Cloud Streets
The cloud patterns illustrated by this image exhibits a double periodicity.
These types of clouds usually occur close to the northern-polar
cap and in the Tharsis and Syria Planum regions.
(Courtesy Calvin J. Hamilton)
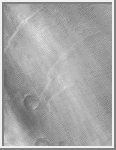 Streaky Clouds
Streaky Clouds
Streaky clouds seem to be found most everywhere; however, they seem to
be more concentrated in the highlands southwest of Syrtis Major.
(Courtesy Calvin J. Hamilton)
 Fog
Fog
Fog often appears in low-lying areas. It typically occurs in the
southern hemisphere especially in the Argyre and Hellas basins.
It forms frequently in craters. Occasionally, it occurs in higher regions
such as Sinus Sabaeus and Solis Planum.
(Courtesy Calvin J. Hamilton)
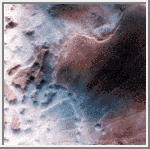 Clouds in Noctis Labyrinthis
Clouds in Noctis Labyrinthis
This image shows early morning fog in the Noctis Labyrinthis, at the
westernmost end of Valles Marineris. This fog, which is probably
composed of water ice, is confined primarily to the low-lying troughs,
but occasionally extends over the adjacent plateau. The region shown
is about 300 kilometers (186 miles) across.
(Courtesy NASA/LPI)
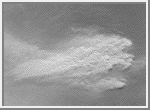 Dust Plume
Dust Plume
This is an example of a dust plume in the Solis Planum region. This
image was taken during the springtime for this region. Plumes are
found primarily in the southern hemisphere, in highlands such
as Syrtis Major and in elevated regions such as Tharsis.
(Courtesy Calvin J. Hamilton)
| References |
|---|
French, Richard et al. "Global Patterns in Cloud Forms on Mars." ICARUS 45, 1981, 32-43.
Carr M. H. The Surface of Mars. Yale University Press, New Haven, 1981. (See Chapter 3, pp. 25-34.)
Kiefer, Walter S., Allan H. Treiman, and Stephen M. Clifford. The Red Planet: A Survey of Mars - Slide Set. Lunar and Planetary Institute.
Copyright © 1997-2000 by Calvin J. Hamilton. All rights reserved. Privacy Statement.