|
COMETS EARTH JUPITER KUIPER BELT MARS MERCURY METEORITES NEPTUNE OORT CLOUD PLUTO SATURN SOLAR SYSTEM SPACE SUN URANUS VENUS ORDER PRINTS
PHOTO CATEGORIES SCIENCEVIEWS AMERICAN INDIAN AMPHIBIANS BIRDS BUGS FINE ART FOSSILS THE ISLANDS HISTORICAL PHOTOS MAMMALS OTHER PARKS PLANTS RELIGIOUS REPTILES SCIENCEVIEWS PRINTS
|
Related Documents
Download Options
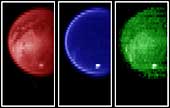
Piercing the ubiquitous layer of smog enshrouding Titan, these images from the Cassini visual and infrared mapping spectrometer reveals an exotic surface covered with a variety of materials in the southern hemisphere. Using near-infrared colors--some three times deeper in the red visible to the human eye--these images reveal the surface with unusual clarity. The left image shows a variety of surface features at a wavelength of 2.0 microns. The darker areas are possibly regions of relatively pure water ice, while the brighter regions likely have a much higher amount of non-ice materials such as simple hydrocarbons. The middle image measured at a wavelength of 2.8 microns shows a very dark surface almost everywhere, as expected for a surface of water ice and simple hydrocarbons. The image on the right, taken at 5.0 microns, is similar to the left image, indicating dark icy regions and brighter hydrocarbon-rich materials. A bright cloud of methane particles is apparent in all three images near the south pole. It's persistence over an extensive range of colors indicates that these cloud particles are large compared to the typical haze particles surrounding the planet, suggesting a dynamically active atmosphere near the South Pole. Color was used to enhance the various wavelengths. |