|
COMETS EARTH JUPITER KUIPER BELT MARS MERCURY METEORITES NEPTUNE OORT CLOUD PLUTO SATURN SOLAR SYSTEM SPACE SUN URANUS VENUS ORDER PRINTS
PHOTO CATEGORIES SCIENCEVIEWS AMERICAN INDIAN AMPHIBIANS BIRDS BUGS FINE ART FOSSILS THE ISLANDS HISTORICAL PHOTOS MAMMALS OTHER PARKS PLANTS RELIGIOUS REPTILES SCIENCEVIEWS PRINTS
|
Related Documents
Download Options
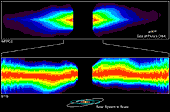
These two Hubble Space Telescope visible-light views of the edge-on disk of dust around the star Beta Pictoris yield telltale evidence for the existence of planets, and possibly the gravitational tug of a companion brown dwarf or bypassing star. Both views reveal warps in the disk that might be caused by the gravitational pull of one or more unseen companions. Since its discovery, Beta Pictoris has long been considered one of the nearest examples of an extrasolar planetary system still forming. The "false color" images show gradations in the brightness of the disk, caused simply by the fact that the disk shines by reflected starlight, and so the farther the dust is from the central star, the fainter it is. In both views the bright glare of the central star is blocked by a black strip that divides the disk into left (east) and right (west) components. Because the disk is tilted nearly edge-on to Earth the images show a sharp, bright, straight ridge extending over the entire length of the disk.(in our solar system this feature is seen as zodiacal light, where sunlight is reflected by a concentration of dust in the ecliptic plane). The orbits of the planets of our solar system are added for scale. [TOP] - This Wide Field Planetary Camera 2 image shows the full extent of the disk, which spans 140 billion miles (1500 astronomical units) edge-to-edge. An unusual flaring at the top of the right side of the disk (the Southwest side of the disk) shows that dust has been pulled above the dense plane of the disk beyond what is observed in the left side. A gravitational perturbation by an unseen substellar- mass companion farther from the star than planets would be, or a tug from a bypassing star might cause this flaring. The image was taken on June 22, 1995. Credit: Al Schultz (CSC/STScI, and NASA) [BOTTOM] - An unprecedented detailed close-up view of the inner region of the disk taken with the Space Telescope Imaging Spectrograph shows a warp in the disk. Though this warp was first seen by Hubble in 1995, the new images go closer to the star than ever before to about 1.4 billion miles (15 astronomical units) -- a radius smaller than that of Uranus' orbit. These new details support the presence of one or more planets orbiting the star. The image was taken in September 1997. Credit: Sally Heap (GSFC/NASA) |