|
COMETS EARTH JUPITER KUIPER BELT MARS MERCURY METEORITES NEPTUNE OORT CLOUD PLUTO SATURN SOLAR SYSTEM SPACE SUN URANUS VENUS ORDER PRINTS
PHOTO CATEGORIES SCIENCEVIEWS AMERICAN INDIAN AMPHIBIANS BIRDS BUGS FINE ART FOSSILS THE ISLANDS HISTORICAL PHOTOS MAMMALS OTHER PARKS PLANTS RELIGIOUS REPTILES SCIENCEVIEWS PRINTS
|
Related Documents
Download Options
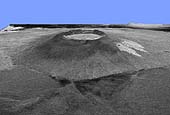
This is a three-dimensional view of Isabela, one of the Galapagos Islands located off the western coast of Ecuador, South America. This view was constructed by overlaying a Spaceborne Imaging Radar-C/X-band Synthetic Aperture Radar (SIR-C/X-SAR) image on a digital elevation map produced by TOPSAR, a prototype airborne interferometric radar which produces simultaneous image and elevation data. The vertical scale in this image is exaggerated by a factor of 1.87. The SIR-C/X-SAR image was taken on the 40th orbit of space shuttle Endeavour. The image is centered at about 0.5 degree south latitude and 91 degrees west longitude and covers an area of 75 by 60 kilometers (47 by 37 miles). The radar incidence angle at the center of the image is about 20 degrees. The western Galapagos Islands, which lie about 1,200 kilometers (750 miles) west of Ecuador in the eastern Pacific, have six active volcanoes similar to the volcanoes found in Hawaii and reflect the volcanic processes that occur where the ocean floor is created. Since the time of Charles Darwin's visit to the area in 1835, there have been more than 60 recorded eruptions on these volcanoes. This SIR-C/X-SAR image of Alcedo and Sierra Negra volcanoes shows the rougher lava flows as bright features, while ash deposits and smooth pahoehoe lava flows appear dark. Vertical exaggeration of relief is a common tool scientists use to detect relationships between structure (for example, faults, and fractures) and topography. |