|
COMETS EARTH JUPITER KUIPER BELT MARS MERCURY METEORITES NEPTUNE OORT CLOUD PLUTO SATURN SOLAR SYSTEM SPACE SUN URANUS VENUS ORDER PRINTS
PHOTO CATEGORIES SCIENCEVIEWS AMERICAN INDIAN AMPHIBIANS BIRDS BUGS FINE ART FOSSILS THE ISLANDS HISTORICAL PHOTOS MAMMALS OTHER PARKS PLANTS RELIGIOUS REPTILES SCIENCEVIEWS PRINTS
|
Related Documents
Download Options
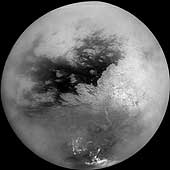
A mosaic of nine processed images recently acquired during Cassini's first very close flyby of Saturn's moon Titan on Oct. 26, 2004, constitutes the most detailed full-disc view of the mysterious moon. The view is centered on 15 degrees South latitude, and 156 degrees West longitude. Brightness variations across the surface and bright clouds near the south pole are easily seen. The images that comprise the mosaic have been processed to reduce the effects of the atmosphere and to sharpen surface features. The mosaic has been trimmed to show only the illuminated surface and not the atmosphere above the edge of the moon. The Sun was behind Cassini so nearly the full disc is illuminated. Pixels scales of the composite images vary from 2 to 4 kilometers per pixel (1.2 to 2.5 miles per pixel). Surface features are best seen near the center of the disc, where the spacecraft is looking directly downwards; the contrast becomes progressively lower and surface features become fuzzier towards the outside, where the spacecraft is peering through haze, a circumstance that washes out surface features. The brighter region on the right side and equatorial region is named Xanadu Regio. Scientists are actively debating what processes may have created the bizarre surface brightness patterns seen here. The images hint at a young surface with, no obvious craters. However, the exact nature of that activity, whether tectonic, wind-blown, fluvial, marine, or volcanic is still to be determined. The images comprising this mosaic were acquired from distances ranging from 650,000 kilometers (400,000 miles) to 300,000 kilometers (200,000 miles). |