|
COMETS EARTH JUPITER KUIPER BELT MARS MERCURY METEORITES NEPTUNE OORT CLOUD PLUTO SATURN SOLAR SYSTEM SPACE SUN URANUS VENUS ORDER PRINTS
PHOTO CATEGORIES SCIENCEVIEWS AMERICAN INDIAN AMPHIBIANS BIRDS BUGS FINE ART FOSSILS THE ISLANDS HISTORICAL PHOTOS MAMMALS OTHER PARKS PLANTS RELIGIOUS REPTILES SCIENCEVIEWS PRINTS
|
Related Documents
Download Options
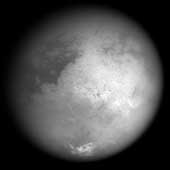
This image taken on Oct. 24, 2004, reveals Titan's bright "continent-sized" terrain known as Xanadu. It was acquired with the narrow angle camera on Cassini's imaging science subsystem through a spectral filter centered at 938 nanometers, a wavelength region at which Titan's surface can be most easily detected. The surface is seen at a higher contrast than in previously released imaging science subsystem images due to a lower phase angle (Sun-Titan-Cassini angle), which minimizes scattering by the haze. The image shows details about 10 times smaller than those seen from Earth. Surface materials with different brightness properties (or albedos) rather than topographic shading are highlighted. The image has been calibrated and slightly enhanced for contrast. It will be further processed to reduce atmospheric blurring and to optimize mapping of surface features. The origin and geography of Xanadu remain mysteries at this range. Bright features near the south pole (bottom) are clouds. On Oct. 26, Cassini will acquire images of features in the central-left portion of this image from a position about 100 times closer. |