|
COMETS EARTH JUPITER KUIPER BELT MARS MERCURY METEORITES NEPTUNE OORT CLOUD PLUTO SATURN SOLAR SYSTEM SPACE SUN URANUS VENUS ORDER PRINTS
PHOTO CATEGORIES SCIENCEVIEWS AMERICAN INDIAN AMPHIBIANS BIRDS BUGS FINE ART FOSSILS THE ISLANDS HISTORICAL PHOTOS MAMMALS OTHER PARKS PLANTS RELIGIOUS REPTILES SCIENCEVIEWS PRINTS
|
Related Documents
Download Options
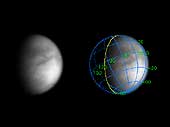
The Cassini spacecraft has beamed back a new, more detailed image of smog-enshrouded Titan. This view represents an improvement in resolution of nearly three times over the previous Cassini image release of Titan (see PIA05392). The superimposed coordinate system grid in the accompanying image at right illustrates the geographical regions of the moon that are illuminated and visible, as well as the orientation of Titan. North is up and rotated 25 degrees to the left. The yellow curve marks the position of the boundary between day and night on Titan. This image shows about one quarter of Titan's surface, from 0 to 70 degrees West longitude, and just barely overlaps part of the surface shown in the previous Titan image release. Most of the visible surface in this image has not yet been shown in any Cassini image. The image was obtained with the narrow angle camera on June 14, 2004, at a phase, or Sun-Titan-spacecraft, angle of 61 degrees and at a distance of 10.4 million kilometers (6.5 million miles) from Titan. The image scale is 62 kilometers (39 miles) per pixel. The image was magnified by a factor of two using a linear interpolation scheme. No further processing to remove the effects of the overlying atmosphere has been performed. The observed brightness variations are real, on scales of one hundred kilometers or less. The image was obtained in the near-infrared (centered at 938 nanometers) through a polarizing filter. The combination was designed to reduce the obscuration by atmospheric haze. The haze is more transparent at 938 nanometers than at shorter wavelengths, and light of 938 nanometers wavelength is not absorbed by methane gas in Titan's atmosphere. Light at this wavelength consequently samples the surface, and the polarizer blocks out light scattered mainly by the haze. This is similar to the way a polarizer, put on the front of a lens of a hand-held camera, makes distant objects more clear on Earth. |