|
COMETS EARTH JUPITER KUIPER BELT MARS MERCURY METEORITES NEPTUNE OORT CLOUD PLUTO SATURN SOLAR SYSTEM SPACE SUN URANUS VENUS ORDER PRINTS
PHOTO CATEGORIES SCIENCEVIEWS AMERICAN INDIAN AMPHIBIANS BIRDS BUGS FINE ART FOSSILS THE ISLANDS HISTORICAL PHOTOS MAMMALS OTHER PARKS PLANTS RELIGIOUS REPTILES SCIENCEVIEWS PRINTS
|
Related Documents
Download Options
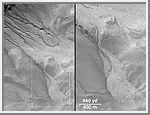
This suite of Mars Global Surveyor (MGS) Mars Orbiter Camera (MOC) pictures provides a vista of martian gullies on the northern wall of a 12 kilometer-(7.4 mile)-wide meteor impact crater east of the Gorgonum Chaos region on the red planet. The first picture (above left) is a composite of three different high resolution MOC views obtained in 1999 and 2000. The second picture (above right) shows the location of the high resolution views relative to the whole crater as it appeared in the highest resolution image previously acquired of the area, taken by the Viking 1 orbiter in 1978. The release image (top) shows a close-up of one of the channels and debris aprons found in the northwestern quarter of the impact crater. Some of the channels in this crater are deeply-entrenched and cut into lighter-toned deposits. The numerous channels and apron deposits indicate that many tens to hundreds of individual events involving the flow of water and debris have occurred here. The channels and aprons have very crisp, sharp relief and there are no small meteor impact craters on them, suggesting that these features are extremely young relative to the 4.5 billion year history of Mars. It is possible that these landforms are still being created by water seeping from the layered rock in the crater wall today. The crater has no name and it is located near 37.4°S, 168.0°W. The composite view in (above left) includes a picture taken by MOC on September 10, 1999, a picture obtained April 26, 2000, and another on May 22, 2000. The scene from left to right (including the dark gap between photos) covers an area approximately 7.6 kilometers (4.7 miles) wide by 18 km (11.1 mi) long. Sunlight illuminates the scene from the upper left. MOC high resolution images are taken black-and-white (grayscale); the color seen here has been synthesized from the colors of Mars observed by the MOC wide angle cameras and by the Viking Orbiters in the late 1970s. |