|
COMETS EARTH JUPITER KUIPER BELT MARS MERCURY METEORITES NEPTUNE OORT CLOUD PLUTO SATURN SOLAR SYSTEM SPACE SUN URANUS VENUS ORDER PRINTS
PHOTO CATEGORIES SCIENCEVIEWS AMERICAN INDIAN AMPHIBIANS BIRDS BUGS FINE ART FOSSILS THE ISLANDS HISTORICAL PHOTOS MAMMALS OTHER PARKS PLANTS RELIGIOUS REPTILES SCIENCEVIEWS PRINTS
|
Related Document
Download Options
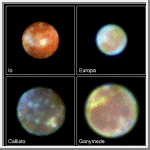
This is a Hubble Space Telescope "family portrait" of the four largest moons of Jupiter (Ganymede, Callisto, Io, Europa), first observed by the Italian scientist Galileo Galilei nearly four centuries ago. Located approximately one-half billion miles away, the moons are so small that, in visible light, they appear as fuzzy disks in the largest ground-based telescopes. Hubble can resolve surface details seen previously only by the Voyager spacecraft in the early 1980s. While the Voyagers provided close-up snapshots of the satellites, Hubble can now follow changes on the moons and reveal other characteristics at ultraviolet and near-infrared wavelengths. Over the past year Hubble has charted new volcanic activity on Io's active surface, found a faint oxygen atmosphere on the moon Europa, and identified ozone on the surface of Ganymede. Hubble ultraviolet observations of Callisto show the presence of fresh ice on the surface that may indicate impacts from micrometeorites and charged particles from Jupiter's magnetosphere. Hubble observations will play a complementary role when the Galileo spacecraft arrives at Jupiter in December of this year. Credit: K. Noll (STScI), J. Spencer (Lowell Observatory), and NASA. |